 Indonesia is the world’s fourth most populous country, and its infrastructure is developing rapidly to meet the growing needs of its urban population and various industries. Bali, Indonesia is one of the most popular tourist destinations in the world, and its water infrastructure is rapidly developing to satisfy the growing needs of its tourism industry. To meet the growing water demand in the Sanur beach resort on Bali’s southeastern coast, the Indonesian government’s, Ministry of Public Works and Public Housing (PU) planned to build the new Petanu water treatment plant. The Indonesian state-owned plant builder, PT Waskita Karya (Persero) Tbk, constructed the plant.
Indonesia is the world’s fourth most populous country, and its infrastructure is developing rapidly to meet the growing needs of its urban population and various industries. Bali, Indonesia is one of the most popular tourist destinations in the world, and its water infrastructure is rapidly developing to satisfy the growing needs of its tourism industry. To meet the growing water demand in the Sanur beach resort on Bali’s southeastern coast, the Indonesian government’s, Ministry of Public Works and Public Housing (PU) planned to build the new Petanu water treatment plant. The Indonesian state-owned plant builder, PT Waskita Karya (Persero) Tbk, constructed the plant.
The Petanu water Treatment plant is dedicated to set a new level of water supply operation in Indonesia. Instrumentation and automation technology is introduced to improve its operational accountability as well as the easiness of its manageability for the operator. SCADA system is the appropriate measure to reach the goal. The Petanu water treatment plant started its commercial operation in May 2014 and produces 300 liters per second (approximately 25,920 cubic meters per day) of drinking water. The plant will increase its production progressively to supply drinking water for three municipalities in Southern Bali (Gianyar, Denpasar and Badung).
The PU and Waskita Karya selected Yokogawa’s process automation system as a one stop solution which includes FAST/TOOLS™ SCADA (supervisory control and data acquisition) system, STARDOM™ network-based control system, and various field instruments. To meet the urgent market demands, PU and Waskita Karya requested Yokogawa Indonesia to deliver these instruments and systems within three months from the order. Furthermore, PU and Yokogawa are committed to support the capacity building for the operator in the Petanu water treatment plant, especially in operating and maintaining SCADA system.
Designers Sneakers
 Following an accidental fire at the IOCL Jaipur Terminal, an extensive review of safety measures recommended by the MB Lal Committee has resulted in the introduction of failsafe actuators for critical tank farm applications. These valves, known as ROSOV (Remote Operated Shut-off Valves), now provide tank overfill protection at the majority of storage facilities owned by the Indian oil industry.
Following an accidental fire at the IOCL Jaipur Terminal, an extensive review of safety measures recommended by the MB Lal Committee has resulted in the introduction of failsafe actuators for critical tank farm applications. These valves, known as ROSOV (Remote Operated Shut-off Valves), now provide tank overfill protection at the majority of storage facilities owned by the Indian oil industry. South Korea’s petrochemical company is located in the town of Yeosu. The plant started from 350,000 tons of ethylene per year production and expanded to 1,000,000 tons per year now. There are twelve naphtha cracking furnaces in this plant. The naphtha used as the feedstock for this plant is fed to a pyrolysis (steam cracking) furnace, where it is combined with steam and heated to 980 to 1,080° C. Within this temperature range, the feedstock molecules "crack" to produce ethylene as well as methane, hydrogen, ethylene, propylene, butadiene, benzene, toluene, xylene, and other co-products. After the pyrolysis reaction is quenched, the rest of the plant separates the desired products into streams that meet the various product specifications. The process steps include distillation, compression, process gas drying, hydrogenation (of acetylenes), and heat transfer.
South Korea’s petrochemical company is located in the town of Yeosu. The plant started from 350,000 tons of ethylene per year production and expanded to 1,000,000 tons per year now. There are twelve naphtha cracking furnaces in this plant. The naphtha used as the feedstock for this plant is fed to a pyrolysis (steam cracking) furnace, where it is combined with steam and heated to 980 to 1,080° C. Within this temperature range, the feedstock molecules "crack" to produce ethylene as well as methane, hydrogen, ethylene, propylene, butadiene, benzene, toluene, xylene, and other co-products. After the pyrolysis reaction is quenched, the rest of the plant separates the desired products into streams that meet the various product specifications. The process steps include distillation, compression, process gas drying, hydrogenation (of acetylenes), and heat transfer. The branch of the largest professional education complex in Latin America, Servico Nacional de Aprendizagem Industrial (SENAI), in Portuguese language for National Service for Industrial Training, provides students with a unique opportunity of learning and gaining practical experience on an actual process with their Yokogawa instrumented micro plants. "Yokogawa is not just providing the products, but also providing all the necessary training and knowledge", said, Mr. Jean Barbosa Cavalcante, the leader of CIITEC, Centro de Inspiracao e Inovacao Tecnologica in Portuguese for Technical Innovation and Inspiration Center from SENAI-AL.
The branch of the largest professional education complex in Latin America, Servico Nacional de Aprendizagem Industrial (SENAI), in Portuguese language for National Service for Industrial Training, provides students with a unique opportunity of learning and gaining practical experience on an actual process with their Yokogawa instrumented micro plants. "Yokogawa is not just providing the products, but also providing all the necessary training and knowledge", said, Mr. Jean Barbosa Cavalcante, the leader of CIITEC, Centro de Inspiracao e Inovacao Tecnologica in Portuguese for Technical Innovation and Inspiration Center from SENAI-AL.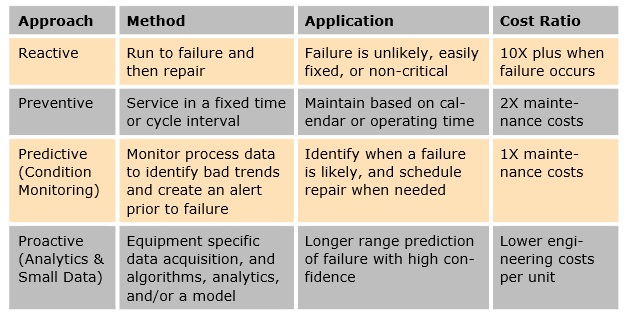 Manufacturers in both the process and discrete manufacturing industries should consider condition monitoring (CM) for critical assets to improve the effectiveness of their maintenance resources. Typical benefits include improved uptime, asset longevity, cost control, yield/quality and safety. A study by a major petroleum company showed that, compared to calendar-based preventive maintenance, predictive reduces maintenance costs by 50 percent. This paper discusses the advantages of packaged predictive maintenance (PdM) applications to leverage existing process and smart device data.
Manufacturers in both the process and discrete manufacturing industries should consider condition monitoring (CM) for critical assets to improve the effectiveness of their maintenance resources. Typical benefits include improved uptime, asset longevity, cost control, yield/quality and safety. A study by a major petroleum company showed that, compared to calendar-based preventive maintenance, predictive reduces maintenance costs by 50 percent. This paper discusses the advantages of packaged predictive maintenance (PdM) applications to leverage existing process and smart device data.