 Honeywell and Palo Alto Networks® are collaborating to boost the cyber security capabilities of control systems used by industrial facilities and critical infrastructure. Honeywell's Industrial Cyber Security business is now offering the Palo Alto Networks Next-Generation Security Platform to industrial customers. The collaboration enables customers to better prevent cyber attacks against their Process Control Networks (PCN) and Operational Technology (OT) environments in order to protect their assets and maximize production uptime and safety.
Honeywell and Palo Alto Networks® are collaborating to boost the cyber security capabilities of control systems used by industrial facilities and critical infrastructure. Honeywell's Industrial Cyber Security business is now offering the Palo Alto Networks Next-Generation Security Platform to industrial customers. The collaboration enables customers to better prevent cyber attacks against their Process Control Networks (PCN) and Operational Technology (OT) environments in order to protect their assets and maximize production uptime and safety.
The joint solution offers unrivaled process network traffic monitoring and advanced threat prevention across the automation environment. It combines Palo Alto Networks' advanced and natively integrated security platform with Honeywell's unique process control domain expertise to provide a cyber security solution tailored for industrial customers. This next-generation offering enhances Honeywell's comprehensive portfolio of cyber security solutions, including its Industrial Cyber Security Risk Manager platform.
Jeff Zindel, vice president and general manager, cyber security, Honeywell Process Solutions said, "The collaboration with Palo Alto Networks expands our ability to provide proactive intrusion prevention resulting in more robust protection for our customers. It is an example of Honeywell's unique multi-vendor approach that integrates state-of-the-art technology with proven expertise so that customers can confidently rely on our cyber security capabilities, quickly and effectively prevent threats, and focus on their daily operations."

 This white paper describes the distinction between failure rate prediction and estimation methods in general and then gives an overview of the procedures used to obtain dangerous failure rates for certain mechanical equipment using exida FMEDA predictions and OREDA estimations. exida frequently compares field failure rate data from various sources to FMEDA results in order to validate the FMEDA component library. However, because OREDA and FMEDA methods are quite different, it is not possible to compare their results directly. A methodology is presented which creates predictions and estimations that are more comparable. The methodology is then applied to specific equipment combinations and the results are compared. When differences in the results exist between the two methods, plausible explanations for the differences are provided.
This white paper describes the distinction between failure rate prediction and estimation methods in general and then gives an overview of the procedures used to obtain dangerous failure rates for certain mechanical equipment using exida FMEDA predictions and OREDA estimations. exida frequently compares field failure rate data from various sources to FMEDA results in order to validate the FMEDA component library. However, because OREDA and FMEDA methods are quite different, it is not possible to compare their results directly. A methodology is presented which creates predictions and estimations that are more comparable. The methodology is then applied to specific equipment combinations and the results are compared. When differences in the results exist between the two methods, plausible explanations for the differences are provided.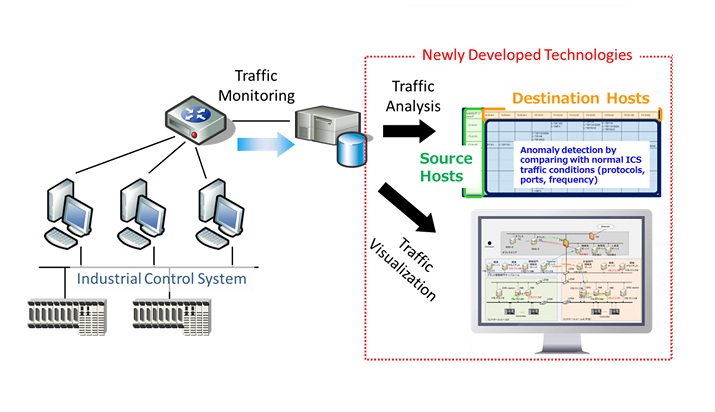 Yokogawa Electric Corporation (Yokogawa, President: Takashi Nishijima) announces that it has worked with the National Institute of Information and Communications Technology of Japan (NICT, President: Dr. Masao Sakauchi), Professor Yasuo Okabe of Kyoto University, and former Associate Professor Hiroki Takakura of Kyoto University to jointly develop a technology that visualizes and analyzes control system traffic to verify its integrity. This technology, which has been integrated by Yokogawa in an industry-first network healthiness check service, can quickly detect security incidents such as a malware infection. This combines visualization technology with the collection and analysis of traffic data to verify the integrity of control system networks, and is expected to improve the security of control systems used in public utilities.
Yokogawa Electric Corporation (Yokogawa, President: Takashi Nishijima) announces that it has worked with the National Institute of Information and Communications Technology of Japan (NICT, President: Dr. Masao Sakauchi), Professor Yasuo Okabe of Kyoto University, and former Associate Professor Hiroki Takakura of Kyoto University to jointly develop a technology that visualizes and analyzes control system traffic to verify its integrity. This technology, which has been integrated by Yokogawa in an industry-first network healthiness check service, can quickly detect security incidents such as a malware infection. This combines visualization technology with the collection and analysis of traffic data to verify the integrity of control system networks, and is expected to improve the security of control systems used in public utilities.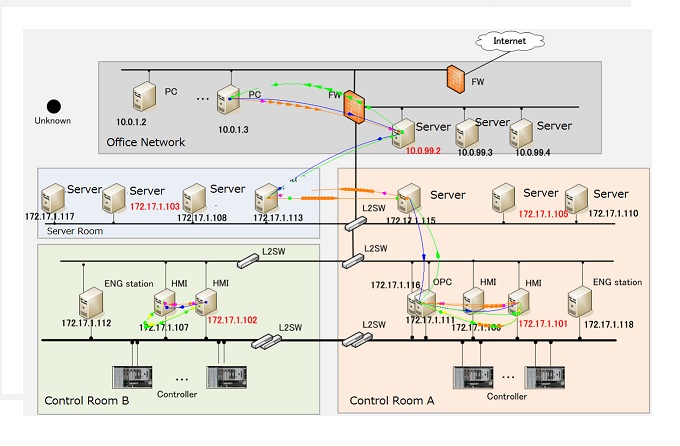
 wa Electric Corporation announces that Yokogawa Solution Service Corporation, a subsidiary that is responsible for Yokogawa's control business in Japan, has taken an order from Asahi Kasei Chemicals Corp. to provide a network healthiness check service that analyzes and verifies the integrity of the data traffic on the control system communications busses at its Mizushima Works. An industry first*, this cyber security service for control systems combines network visualization technology with the collection and analysis of data traffic.
wa Electric Corporation announces that Yokogawa Solution Service Corporation, a subsidiary that is responsible for Yokogawa's control business in Japan, has taken an order from Asahi Kasei Chemicals Corp. to provide a network healthiness check service that analyzes and verifies the integrity of the data traffic on the control system communications busses at its Mizushima Works. An industry first*, this cyber security service for control systems combines network visualization technology with the collection and analysis of data traffic. Exida, a global supplier of functional safety products, services, and certifications has released their Safety Equipment Reliability Handbook (SERH) – 4th Edition, a hard copy of the SERH database with a vast amount of equipment item reliability data.
Exida, a global supplier of functional safety products, services, and certifications has released their Safety Equipment Reliability Handbook (SERH) – 4th Edition, a hard copy of the SERH database with a vast amount of equipment item reliability data.